



































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An in-depth analysis of the kinematics of differential and synchro drives, focusing on forward and inverse kinematics. It covers topics such as system measurements, determining the robot's velocity and position, the instantaneous center of curvature, and solving equations for desired velocities. The document also discusses various wheeled robots and their kinematic challenges.
Typology: Slides
1 / 45

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






































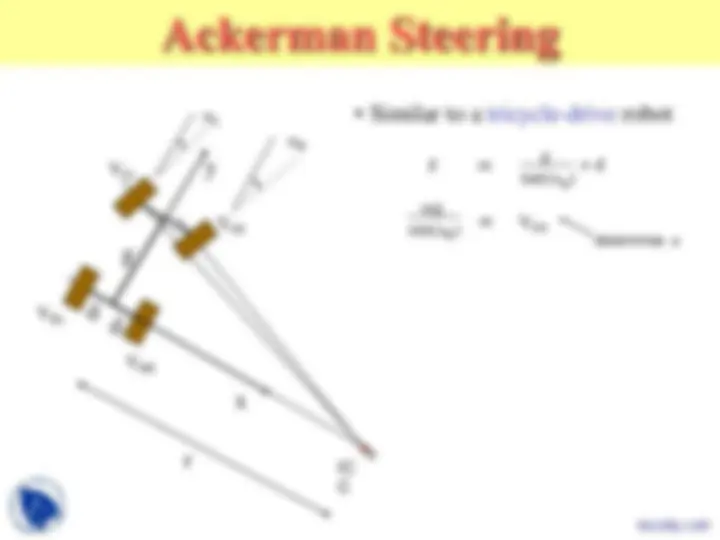
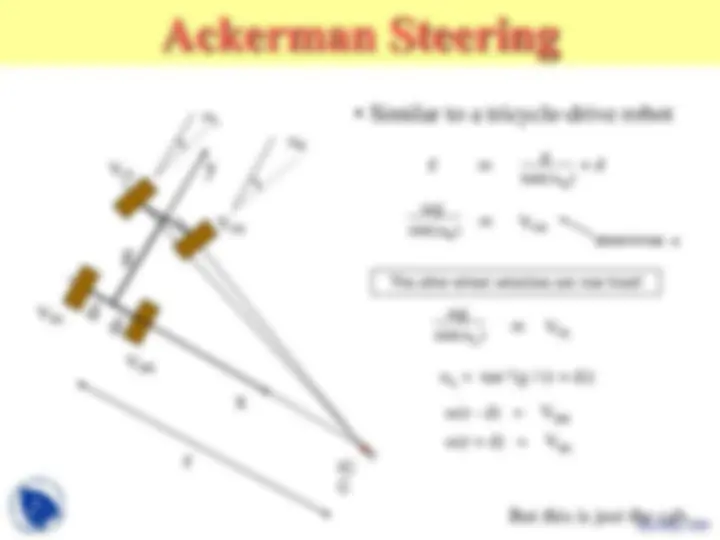
Other mini machines
radio unit linear vision gripper video 55mm dia. base
(assume a wheel radius of 1)
q 2d
(assume a wheel radius of 1)
q 2d
(assume a wheel radius of 1)
q 2d
(assume a wheel radius of 1) 2d
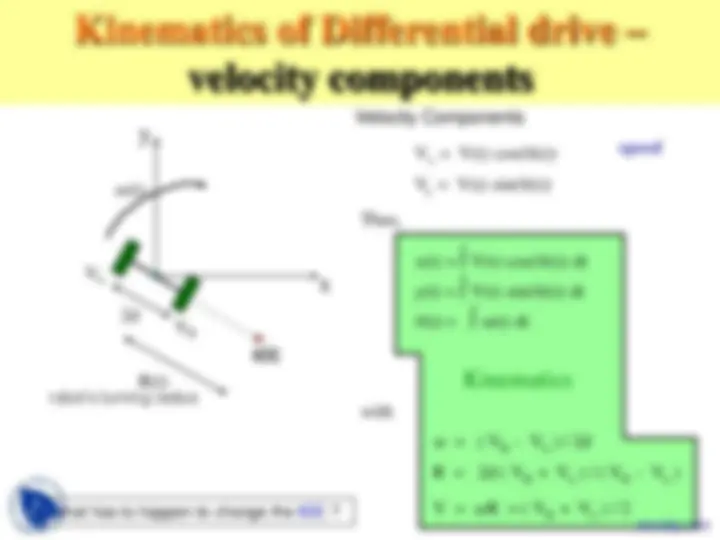
Kinematics of Differential drive ICC “instantaneous center of curvature”
2d
So, the robot’s velocity is (^) V = wR = ( V R + VL ) / 2 Kinematics of Differential drive – robot’s velocity
2d ICC R(t) robot’s turning radius w(t) w = ( VR - VL ) / 2d R = 2d ( VR + VL ) / ( VR - VL ) V = wR = ( VR + VL ) / 2 Vx = V(t) cos(q(t)) Vy = V(t) sin(q(t)) with
Thus, Kinematics of Differential drive
Velocity Components VR
2d ICC R(t) robot’s turning radius w(t) Thus, w = ( VR - VL ) / 2d R = 2d ( VR + VL ) / ( VR - VL ) What has to happen to change the ICC?^ V^ =^ wR = ( VR + VL ) / 2 Vx = V(t) cos(q(t)) Vy = V(t) sin(q(t))
with
Kinematics of Differential drive – velocity components speed
Where is the ICC? Kinematics of Synchro drive – wheels synchronized
q w Vwheels
robot
wheels
robot
wheels
position velocity simpler to control, but ... ICC at Kinematics of Synchro drive – velocity and position
Synchro Drive using Lego more difficult to build. this light sensor follows the direction of the wheels, but the RCX is stationary also, four bump sensors and two motor encoders are included But how do we get somewhere? docsity.com
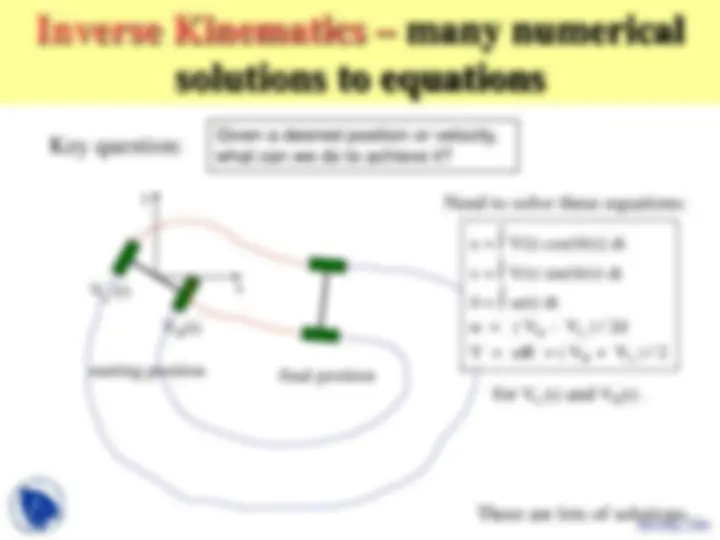
Inverse Kinematics of Differential Drive