














Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Some concept of Turbomachinery Aerodynamics are Axial Flow Compressors, Axial Turbine Design Considerations, Blade Performance, Engine Performance Significantly, Flows Through Axial Compresso. Main points of this lecture are: Transonic Compressors, Subsonic, Axial Compressor, Chord Wise, Wise Direction, Subsonic, Rotor Exit, Large Diffusion, Supersonic Entry, Utilize Supersonic
Typology: Slides
1 / 21

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!














1
Normally a transonic compressor has either V 1 or C 2 supersonic
V 1 or C (^2) may be supersonic at tip or at many sections of the blade
CDA Blades :
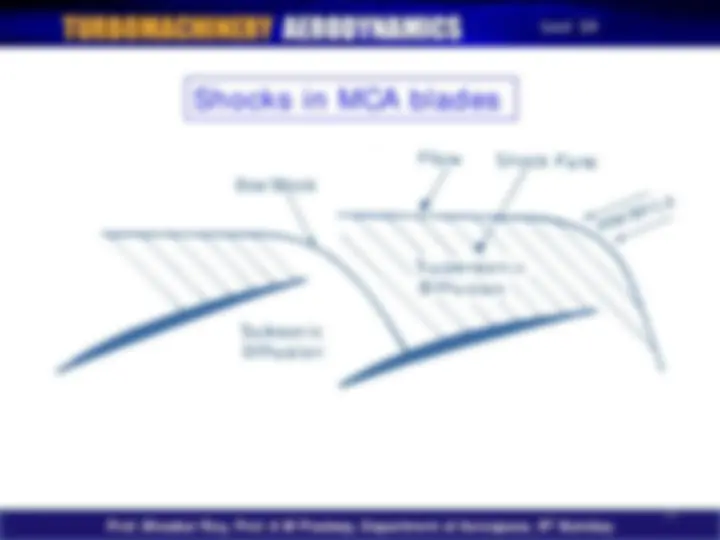
Flow through a transonic blading would diffuse through the shocks before further diffusing and exiting as subsonic flow
DCA blades
Flow through S-type blades has minimal camber but high supersonic diffusion
DCA Blades :
MCA Blades :
When a designer tries to maximize the absolute total pressure ratio by increasing the total temperature ratio, the relative total pressure ratio falls, depending on the design point efficiency chosen based on state of art of design capability available at hand.