













































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
A detailed overview of the gas collection station (gcs) and gas compression plant (gcp) located in kalol, india. It covers the key components, processes, and objectives of these facilities. The gcs is responsible for collecting natural gas from wells and associated gas from the gas-gathering station (ggs), while the gcp compresses the collected gas to high pressure for further distribution. The document delves into the specific equipment used, such as manifolds, scrubbers, and compressors, as well as the overall gas flow and processing within the system. It also touches on the fire-fighting system, effluent treatment, and other ancillary facilities that support the operations. This comprehensive information provides valuable insights into the infrastructure and operations of a gas collection and compression system in the oil and gas industry.
Typology: Summaries
1 / 52

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!













































Firstly, we would like thanks Mr. N. Khanduri for his great efforts in arranging our training at Ahmedabad asset under surface team. We would like to express our sincere thanks to installation managers of GGS motera KALOL,C.T.F, G.C.S,G.C.P, KALOL G.G.S VII , E.T.P, C.W.I.P, Nawagam C.T.F, Desalter plant, Artificial lift & security dept. O.N.G.C AHMEDABAD. We express our deepest thanks to Mr. M.G Desai (Head of Chemical Engg Dept.) for providing us the moral support and encouragement, without which it would have been difficult to complete this training. Preface Theory of any subject is important but without its practical knowledge it becomes useless, particularly for technical students. A technical student cannot become a perfect engineer or
TOTAL LIQUID PRODUCTION-40 m^3 /day WATER INJECTION WELLS- nil GAS INJECTED-20000 m^3 /day VESSELS: LOW PRESSURE SEPARATOR- (vol- 6 m^3 ) GROUP SEPARATOR- (vol-6 m^3 ) TEST SEPARATOR- (vol- 6m^3 ) VERTICAL SCRUBBER-(capacity-1.7 lacks m^3 /day) HORIZONTAL SCRUBBER-(capacity- 50000 m^3 /day) BATH HEATER- 1 NO.S TANKS OIL STORAGE TANKS- 3 NO.S (45 m^3 ) FUNCTION: At group gathering system (GGS) fluid from various wells is collected in header from various wells through pipeline network. Then the low pressure fluid (1- 2 kg/cm^2 ) goes to the low pressure separator, and then in the output we get separated oil and gas. Oil goes directly to storage tanks and gas goes to common sucker separator. On the other hand fluid of 4-5 kg/cm^2 pressure goes to group separator. Then from the outlet of this separator gas goes to common suction separator and oil goes directly to storage tanks. Then in common suction separator all the gases from the outlet of group separator and low pressure separator is further separated, thus if any amount of oil is still present in gas can be separated. So after separation gas is directly sent to GAIL and oil goes to storage tank.
When the fluids coming out of the wells have pressure of about 1-2 kg/cm^2 then fluid goes to this separator. All these separators have same capacity.
4. VALVES Gate valves: used to minimize the pressure drop in the open position and stop the flow rather than controlling it Check valves: it is one-way valve which normally allow fluid to flow through it in only one direction. This prevents the back flow of fluid into wells. 5. STORAGE SYSTEM Purpose: To store oil before transporting To measure oil produced Process: Oil from bath heater and separator is taken into overhead cylindrical tanks for measurement. 6. OIL DISPATCH SYSTEM Purpose: To dispatch oil from GGS to CTF. Process: Oil stored in the storage tanks is sent to CTF by road tanker as there is no pumping system available in the installation. 7. BATH HEATER
Used to reduce the viscosity of oil coming from reservoir by heating that oil in bath heater.
8. FIRE FIGHTING SYSTEM Large water tank- (capacity- 350 m^3 ) Small water tank- (capacity- 100m^3 )
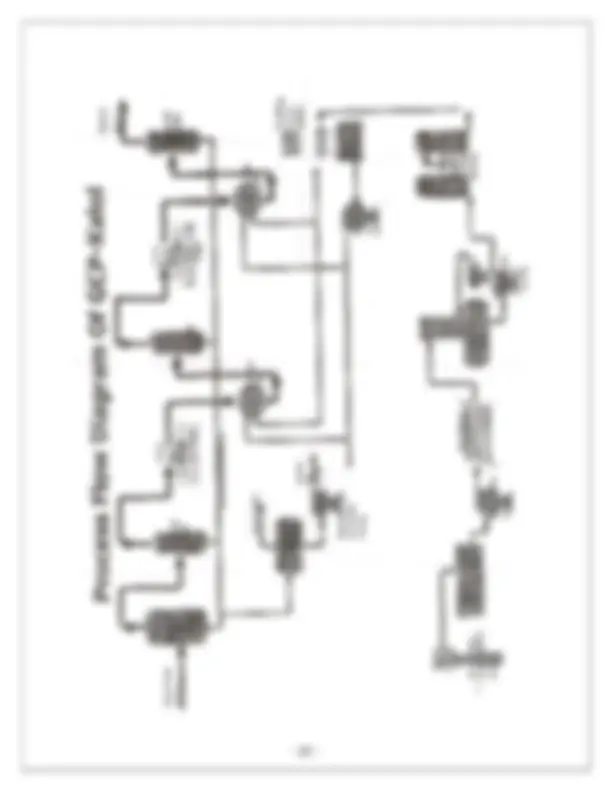
INSTALLATION MANAGER : Mr.B.B.Patel ESTABLISHED IN : 1973 RECEIVING STATUS : Total Wells Connected- Total Working Wells- 13 Receiving pressure-4kg/cm^2 OBJECTIVES: To collect natural gas from wells To collect associated gas from GGS To send gas to GCP. To send compressed gas (CG) to GGS for artificial lifting To send CG to IFFCO,RIL, etc. FUNCTIONS: Its main function is gas collection and distribution. GCS receives associated gas from GGS and natural gas directly from the wells. They both are mixed in scrubber, treated and they are transferred to GCP for further compression. Now the compressed gas is again received back by GCS and then the compressed gas is sent to various destinations. GCS FACILITIES
1. MANIFOLDS Gas grid manifold (to provide high pressure compressed gas through 4’’ & 6’’ pipeline to north and south Kalol gas system)
Purpose It is a purifier that removes impurities from gas. Scrubber systems are a diverse group of air pollution control devices that can be used to remove particulates and/or gases from industrial exhaust streams. Traditionally, the term “scrubber” has referred to pollution control devices that use liquid to “scrub” unwanted pollutants from a gas stream. Recently, the term is also used to describe systems that inject a dry reagent or slurry into a dirty exhaust stream to “scrub out” acid gases. Scrubbers are one of the primary devices that control gaseous emissions, especially acid gases. Process It involves the addition of an alkaline material (usually hydrated lime and soda ash) into the gas stream to react with the acid gases. The acid gases react with the alkaline sorbents to form solid salts which are removed in the particulate control devices. These systems can achieve acid gas (SO 2 and HCl) removal efficiencies.
4. SEPARATOR Functions at 4kg/cm^2 In this only natural gas is separated to remove any condensed liquids if present. The gas firstly goes to separator then to scrubber. 5. STORAGE TANK 3 storage tanks of 45m^3 are present but they are not under usage. 6. VALVES Shut down valve-used in case of leakage or in any other emergency Control valves- when pressure in the pipelines increases beyond the limit then these valves get open itself to prevent danger. 7. FLARE
IIFCO (Associated. Gas) 30000m^3 /day SAHAND-II (Natural Gas) 50000m^3 /day Bharat Vijay Mill(Sintex)(Associated Gas) 15000-20000m^3 /day RIL (Compressed Gas) 1 lacks m^3 /day Compressed gas to Grid 4.30 lacks m^3 /day Gurukul (Kalol) 300 m^3 /day Central Farm Tank (CTF) (Associated Gas) 1700m^3 /day
INSTALLATION MANAGER : Mr. Rajesh Kumar DATE OF COMMISION: GCP-I: 26.02. GCP-II: 15.03. TOTAL CAPACITY : 5 lacks m^3 /day TOTAL COMPRESSORS: 10 6 in old plant and 4 in new plant Capacity (old) =3 lacks m^3 /day Capacity (new) = 2 lacks m^3 /day REVERSE-OSMOSIS PLANT (R-O): two DISCHARGE PRESSURE : 40 kg/cm 2 PROCESS DESCRIPTION: In this plant, gas from GCS (gas collecting system) at 4kg/cm^2 pressure comes through pipelines to GCP. Firstly it goes to common inlet separator, where the primary separation is done, usually the content of oil in gas is negligible but if it’s there it gets separated. Now the gas goes to 1st stage suction separator, there further separation is done. Till now the pressure is 4kg/cm^2 , now this gas goes for first stage compression goes into compressor. After compression the gas we get is of 12-14 kg/cm^2 and because of compression temperature rises to 125^0 C so to low down the temperature to 40-45^0 C, compressed gas is sent to inter gas cooler. Now the cooled gas of 12-14 kg/cm^2 pressure goes to 2nd^ stage suction separator where further separation occurs. Then it goes to 2nd^ stage gas compressor there compression is done and in the output we get gas of 40 kg/cm^2 pressure but temperature has again gone up to 145^0 C because of compression so it again goes to cooler which is also known as after cooler. Now as cooling has occur so condensation will be done so again whatever amount of oil will be there will be drained out from discharge separator. Then finally gas from the discharge separator at 40 kg/cm^2 pressure is sent back to GCS. GCP FACILITIES
Two 11 KV sub-station 8 step down transformers